Prediction of Exacerbation Events using myCOPD data.
This is a subtitle for your new post

As Pilot 4, my mhealth and the University of Southampton collaborated to develop a machine learning model to predict and manage worsening of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), termed exacerbation. Results demonstrated that self-reported COPD data, using a digital health app, can be used to identify users at risk of exacerbation within 3 days with moderate discriminative ability
Prediction of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Exacerbation Events by Using Patient Self-reported Data in a Digital Health App: Statistical Evaluation and Machine Learning Approach.
BigMedilytics (Big Data for Medical Analytics) was the largest EU-funded initiative to transform the region’s healthcare sector. Its aim was to enhance patient outcomes and increase productivity in the health sector by applying big data technologies to complex datasets while ensuring security and privacy of personal data.
Twelve pilots across eight countries, more than 11 million healthcare records, and data from other sectors including insurance and public bodies addressed three themes: Population Health and Chronic Disease Management, Oncology and Industrialization of Healthcare Services; and covered the entire Healthcare Continuum from Prevention to Diagnosis, Treatment and Home Care.
As Pilot 4, my mhealth and the University of Southampton collaborated to develop a machine learning model to predict and manage worsening of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), termed exacerbation.
Using the cloud-based digital health application (app) myCOPD, analysis explored several in-app reported variables including medication usage, COPD assessment test scores, and symptom scores. This led to the development of both heuristic and machine learning models.
Results demonstrated that self-reported COPD data, using a digital health app, can be used to identify users at risk of exacerbation within 3 days with moderate discriminative ability (AUROC 0.727, 95% CI 0.720-0.735). Further research utilizing additional linked data (particularly from medical devices such as smart inhalers, physiological monitoring sensors, and environmental sensors) are expected to increase the accuracy of these models.
Data self-reported to health care apps designed to remotely monitor patients with COPD can be used to predict acute exacerbation events with moderate performance. This could increase personalization of care by allowing pre-emptive action to be taken to mitigate the risk of future exacerbation events.
With the Health and Social Care Secretary setting a target for 4 million to benefit from personalised care by March 2024, leveraging the data collected by these apps in prognostic models could provide increased personalization of care by allowing pre-emptive action to be taken to mitigate the risk of future exacerbation events
Findings have been published in the JMIR Medical Informatics:
©Francis P Chmiel, Dan K Burns, John Brian Pickering, Alison Blythin, Thomas MA Wilkinson, Michael J Boniface. Originally published in JMIR Medical Informatics (https://medinform.jmir.org/2022/3/e26499), 21.03.2022.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work, first published in JMIR Medical Informatics, is properly cited. The complete bibliographic information, a link to the original publication onhttps://medinform.jmir.org/, as well as this copyright and license information must be included.
About my mhealth
my mhealth’s digital therapeutics have been prescribed to over 90,000 patients with chronic conditions, resulting in reduced morbidity and hospital admissions. It serves patients across a range of long-term conditions, including COPD, asthma, diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Real world and clinical trial evidence demonstrates the efficacy of digital interventions on the my mhealth platform.
For more information on my mhealth, visit www.mymhealth.com.
Your Feedback, Our Improvements We want to make sure our product is designed with your needs in mind. To achieve this, we regularly send out surveys and work closely with our Patient & Public Involvement (PPI) group, ensuring that your feedback directly shapes improvements and updates. We received 147 responses to our Research Community Survey .. said they found our app easy to use Overall, most of you said you had positive experiences of using the app .. said you would keep using it to manage your condition Our PPI activities have helped us to make important changes... Navigating around isn’t always that easy The home screen menu is now grouped into smaller sections with a ‘To Do’ list to help you stay on track Too many questions at the start makes it just too complicated Most of the questions at the start have now been removed so you can get started sooner We have now expanded the nutrition information which also contains a nutrition questionnaire to provide you with personalised advice There is not enough information on nutrition. Sometimes I forget to eat What we are working on We are creating a ‘Prepare for Your Appointment’ function in myCOPD and myAsthma We are planning to include a ‘Search’ function so you can get to what you need quickly Keep talking to us! Your experiences help us continue to improve.If you would like to share your thoughts or be part of our Patient and Public Involvement group, please join the Research Community. We would love to hear from you

A new partnership between leading digital health innovators, my mhealth and Patients Know Best (PKB) means shared NHS customers can streamline the delivery of their digital care tools, making it easier to empower patients to manage their health effectively. The collaboration brings together my mhealth’s award-winning self-management platforms with PKB’s personal health record solution, which is already embedded within the NHS App. “At the heart of this partnership is the patient,” said Dr. David Pettigrew, CEO of my mhealth . “By aligning our platforms, we’re enabling people to take greater control of their health while supporting clinicians with joined-up, efficient care pathways. It’s a significant step towards the NHS’s vision of a single ‘front door’ for digital health.” Key Benefits for Patients and the NHS: ● One seamless journey: Patients and clinicians benefit from a more unified experience across apps and services. ● Better outcomes through joined-up care: Shared access to data empowers more personalised and timely interventions. ● Greater access to services: Patients can engage with support tools and resources anytime, anywhere. ● Reduced clinical workload: Digitally enhanced care pathways streamline processes and free up clinical time. ● Scalable long-term condition support: Proven tools for managing COPD, asthma, diabetes, and more, integrated with national systems. ● Patient empowerment: Enabling people to be active participants in their health journey. This partnership also honours the early vision of digital health pioneer Dr Warner Slack, who said in the 1970s: “I hoped that the computer would help the doctor in the care of the patient. And in the back of my mind was the idea that the computer might actually help patients to help themselves with their medical problems.” Today , that vision is becoming reality - placing digital tools directly in the hands of patients and enabling a more connected, compassionate, and sustainable NHS. About my mhealth my mhealth provides evidence-based digital therapeutics for patients with long-term conditions including COPD, asthma, diabetes, and heart disease. Trusted by NHS organisations across the UK, their platforms deliver scalable self-management support and remote monitoring tools that improve outcomes and reduce healthcare burden. About Patients Know Best Patients Know Best is the World’s largest Personal Health Record (PHR) and patient engagement platform, integrating data feeds from over 550 health organisations and providers. The system connects information from GPs, hospitals, social and mental health care providers, to create a single, unified copy of patient data. Everything from appointments and letters to test results, care plans, real-time monitoring data and discharge summaries, as well as the patient’s own data, are all available in one patient record, enabling patients and healthcare professionals to access up-to-date health information anytime, anywhere. In the UK, the platform serves over 5 million patients, registering 100,000+ patients and releasing over 20 million test results a month. PKB integrates with the NHS App to provide a single front door for patients to access their information.

NHS University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, part of North Central London ICB, is taking a significant step towards enhancing patient empowerment and optimising disease management. Asthma is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide, often leading to severe health complications if not managed properly. Recognising the critical need for effective self-management tools, NHS University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust has chosen the myAsthma app to provide patients with the resources they need to take control of their health. Dr Kay Roy PhD FRCP, Consultant Respiratory Physician University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, comments “We are thrilled to introduce myAsthma as a self-management tool to our community. It represents a significant step forward in empowering our patients with asthma to take control of their health. By providing them with personalised support, we believe this tool will greatly improve their quality of life. Additionally, the use of myAsthma in outpatient settings will help triage patients more effectively, ensuring they are seen in a timely manner and appropriately referred for the right investigations and services. Our team is excited to see the positive impact this will have on the asthma population across North Central London ICB." The myAsthma app, part of the my mhealth suite of digital health solutions, is designed to empower patients with comprehensive tools and information to manage their asthma more effectively. Key features include: • Personalised Action Plans: Tailored asthma management plans based on individual patient needs. • Inhaler technique training: Contributing to better health outcomes and reduced risk of exacerbations • Medication Tracking: Reminders and logs to ensure patients take their medication as prescribed. • Symptom tracking: Easy-to-use tools for tracking symptoms and triggers. • Educational Resources: Access to a wealth of information on asthma, helping patients understand their condition and how to manage it. As more NHS partners embrace the my mhealth platform, we're thrilled to witness its growing impact and the positive changes it is bringing to long-term condition care. For more information on this article or other my mhealth projects, please get in touch https://mymhealth.com/contact-us

Henry M.G. Glyde1Alison M. Blythin2 Tom M.A. Wilkinson3Ian T. Nabney4 James W. Dodd5 EPSRC Centre for Doctoral Training in Digital Health and Care, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK my mHealth Limited, Bournemouth , UK my mHealth and Clinical and Experimental Science, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK School of Engineering Mathematics and Technology, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK Academic Respiratory Unit, Translational Health Sciences, Bristol Medical School, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK Abstract Background Acute exacerbations of COPD (AECOPD) are episodes of breathlessness, cough and sputum which are associated with the risk of hospitalisation, progressive lung function decline and death. They are often missed or diagnosed late . Accurate timely intervention can improve these poor outcomes. Digital tools can be used to capture symptoms and other clinical data in COPD. This study aims to apply machine learning to the largest available real-world digital dataset to identify AECOPD Prediction tool which could be used to support early intervention improve clinical outcomes. Objective To create and validate a machine learning predictive model that forecasts exacerbations of COPD 1-8 days in advance. The model is based on routine patient-entered data from myCOPD self-management app. Method Adaptations of the AdaBoost algorithm were employed as machine learning approaches. The dataset included 506 patients users between 2017-2021. 55,066 app records were available for stable COPD event labels and 1,263 records of AECOPD event labels. The data used for training the model included COPD assessment test (CAT) scores, symptom scores, smoking history, and previous exacerbation frequency. All exacerbation records used in the model were confined to the 1-8 days preceding a self-reported exacerbation event. Results TheEasyEnsemble Classifier resulted in a Sensitivity of 67.0% and a Specificity of 65% with a positive predictive value (PPV) of 5.0% and a negative predictive value (NPV) of 98.9%. An AdaBoost model with a cost-sensitive decision tree resulted in a a Sensitivity of 35.0% and a Specificity of 89.0% with a PPV of 7.08% and NPV of 98.3%. Conclusion This preliminary analysis demonstrates that machine learning approaches to real-world data from a widely deployed digital therapeutic has the potential to predict AECOPD and can be used to confidently exclude the risk of exacerbations of COPD within the next 8 days. Permission to use received from Henry Glyde. Read more on Heliyon website.
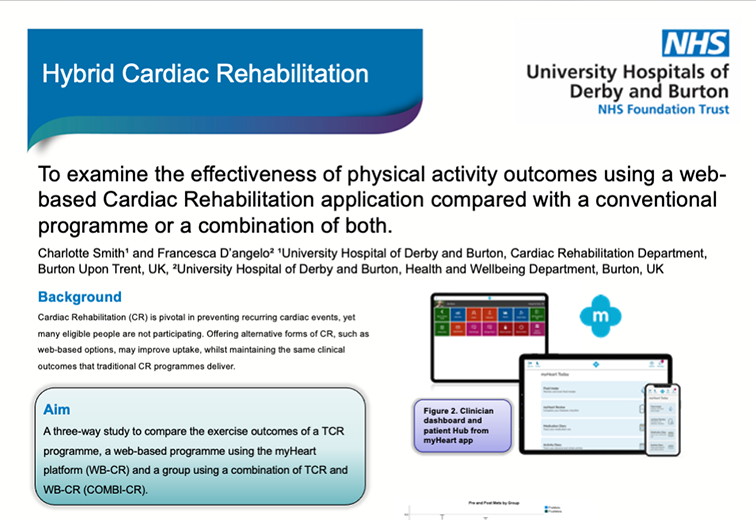
Charlotte Smith 1 Francesca D’angelo 2 University Hospital of Derby and Burton, Cardiac Rehabilitation Department, Burton Upon Trent, UK. University Hospital of Derby and Burton, Health and Wellbeing Department, Burton, UK To examine the effectiveness of physical activity outcomes using a web-based Cardiac Rehabilitation application compared with a conventional programme or a combination of both. University Hospitals of Derby and Burton NHS Foundation Trust poster presented at the BACPR Annual Conference October 5-6th 2023 Permission to use received from Charlotte Smith

Francesca D’angelo 1 Charlotte Smith 2 University Hospital of Derby and Burton, Health and Wellbeing Department, Burton, UK University Hospital of Derby and Burton, Cardiac Rehabilitation Department, Burton Upon Trent, UK. To examine the effectiveness of psychological outcomes using a web-based Cardiac Rehabilitation application compared with a conventional programme or a combination of both. University Hospitals of Derby and Burton NHS Foundation Trust poster presented at the BACPR Annual Conference October 5-6th 2023 Poster presented at the BACPR Annual Conference October 5-6th 2023 Permission to use received from Charlotte Smith